
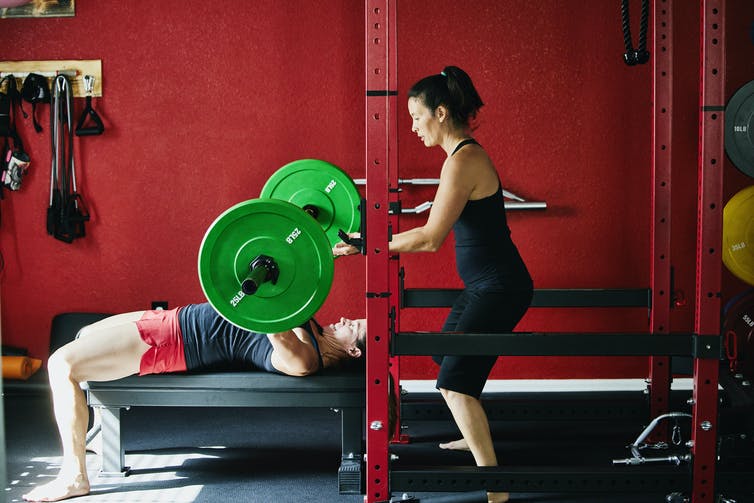
There is perhaps no better way to see the absolute pinnacle of human athletic abilities than by watching the Olympics. But at the Winter Games this year – and at almost all professional sporting events – you rarely see a competitor over 40 years old and almost never see a single athlete over 50. This is because with every additional year spent on Earth, bodies age and muscles don’t respond to exercise the same as they used to.
I lead a team of scientists who study the health benefits of exercise, strength training and diet in older people. We investigate how older people respond to exercise and try to understand the underlying biological mechanisms that cause muscles to increase in size and strength after resistance or strength training.
Old and young people build muscle in the same way. But as you age, many of the biological processes that turn exercise into muscle become less effective. This makes it harder for older people to build strength but also makes it that much more important for everyone to continue exercising as they age.

Thomas Barwick/Digital Vision via Getty Images
Table of Contents
How the body builds muscle
The exercise I study is the type that makes you stronger. Strength training includes exercises like pushups and situps, but also weightlifting and resistance training using bands or workout machines.
When you do strength training, over time, exercises that at first felt difficult become easier as your muscles increase in strength and size – a process called hypertrophy. Bigger muscles simply have larger muscle fibers and cells, and this allows you to lift heavier weights. As you keep working out, you can continue to increase the difficulty or weight of the exercises as your muscles get bigger and stronger.
It is easy to see that working out makes muscles bigger, but what is actually happening to the cells as muscles increase in strength and size in response to resistance training?
J. Gordon Betts, Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter DeSaix via OpenStax, CC BY
Any time you move your body, you are doing so by shortening and pulling with your muscles – a process called contraction. This is how muscles spend energy to generate force and produce movement. Every time you contract a muscle – especially when you have to work hard to do the contraction, like when lifting weights – the action causes changes to the levels of various chemicals in your muscles. In addition to the chemical changes, there are also specialized receptors on the surface of muscle cells that detect when you move a muscle, generate force or otherwise alter the biochemical machinery within a muscle.
In a healthy young person, when these chemical and mechanical sensory systems detect muscle movement, they turn on a number of specialized chemical pathways within the muscle. These pathways in turn trigger the production of more proteins that get incorporated into the muscle fibers and cause the muscle to increase in size.
These cellular pathways also turn on genes that code for specific proteins in cells that make up the muscles contracting machinery. This activation of gene expression is a longer-term process, with genes being turned on or off for several hours after a single session of resistance exercise.
The overall effect of these many exercise-induced changes is to cause your muscles to get bigger.
How older muscles change
While the basic biology of all people, young or old, is more or less the same, something is behind the lack of senior citizens in professional sports. So what changes in a person’s muscles as they age?
What my colleagues and I have found in our research is that in young muscle, a little bit of exercise produces a strong signal for the many processes that trigger muscle growth. In older people’s muscles, by comparison, the signal telling muscles to grow is much weaker for a given amount of exercise.
In a recent study, we wanted to see if the changes in signaling were accompanied by any changes in which genes – and how many of them – respond to exercise. Using a technique that allowed us to measure changes in thousands of genes in response to resistance exercise, we found that when younger men exercise, there are changes in the expression of more than 150 genes. When we looked at older men, we found changes in the expression of only 42 genes. This difference in gene expression seems to explain, at least partly, the more visible variation between how young and old people respond to strength training.

Peathegee Inc via Getty Images
Staying fit as you age
When you put together all of the various molecular differences in how older adults respond to strength training, the result is that older people do not gain muscle mass as well as young people.
But this reality should not discourage older people from exercising. If anything, it should encourage you to exercise more as you age.
Exercise still remains one of the most important activities older adults can do for their health. The work my colleagues and I have done clearly shows that although the responses to training lessen with age, they are by no means reduced to zero.
We showed that older adults with mobility problems who participate in a regular program of aerobic and resistance exercise can reduce their risk of becoming disabled by about 20%. We also found a similar 20% reduction in risk of becoming disabled among people who are already physically frail if they did the same workout program.
While younger people may get stronger and build bigger muscles much faster than their older counterparts, older people still get incredibly valuable health benefits from exercise, including improved strength, physical function and reduced disability. So the next time you are sweating during a workout session, remember that you are building muscle strength that is vital to maintaining mobility and good health throughout a long life.
[Get fascinating science, health and technology news. Sign up for The Conversation’s weekly science newsletter.]
![]()
Roger Fielding receives funding from USDA, NIH, Biophytis, Nestle', Lonza.























