
Dementia is a progressive loss of cognitive abilities, such as memory, that is significant enough to have an impact on a person’s daily activities.
It can be caused by a number of different diseases, including Alzheimer’s, which is the most common form. Dementia is caused by a loss of neurons over a long period of time. Since, by the time symptoms appear, many changes in the brain have already occurred, many scientists are focusing on studying the risk and protective factors for dementia.
A risk factor, or conversely, a protective factor, is a condition or behaviour that increases or reduces the risk of developing a disease, but does not guarantee either outcome. Some risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, such as age or genetics, are not modifiable, but there are several other factors we can influence, specifically lifestyle habits and their impact on our overall health.
These risk factors include depression, lack of physical activity, social isolation, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, as well as poor sleep.
We have been focusing our research on the question of sleep for over 10 years, particularly in the context of the Framingham Heart Study. In this large community-based cohort study, ongoing since the 1940s, the health of surviving participants has been monitored to the present day. As researchers in sleep medicine and epidemiology, we have expertise in researching the role of sleep and sleep disorders in cognitive and psychiatric brain aging.
As part of our research, we monitored and analyzed the sleep of people aged 60 and over to see who did — or did not — develop dementia.
Table of Contents
Sleep as a risk or protective factor against dementia
Sleep appears to play an essential role in a number of brain functions, such as memory. Good quality sleep could therefore play a vital role in preventing dementia.
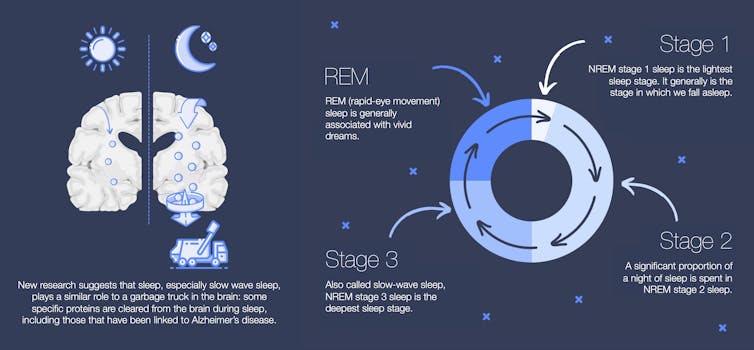
Sleep is important for maintaining good connections in the brain. Recently, research has revealed that sleep seems to have a function similar to that of a garbage truck for the brain: deep sleep could be crucial for eliminating metabolic waste from the brain, including clearing certain proteins, such as those known to accumulate in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
However, the links between deep sleep and dementia still have to be clarified.
What is deep sleep?
During a night’s sleep, we go through several sleep stages that succeed one another and are repeated.
NREM sleep (non-rapid eye movement sleep) is divided into light NREM sleep (NREM1 stage), NREM sleep (NREM2 stage) and deep NREM sleep, also called slow-wave sleep (NREM3 stage). The latter is associated with several restorative functions. Next, REM sleep (rapid eye movement sleep) is the stage generally associated with the most vivid dreams. An adult generally spends around 15 to 20 per cent of each night in deep sleep, if we add up all the periods of NREM3 sleep.
Several sleep changes are common in adults, such as going to bed and waking up earlier, sleeping for shorter periods of time and less deeply, and waking up more frequently during the night.
(Andrée-Ann Baril)
Loss of deep sleep linked to dementia
Participants in the Framingham Heart Study were assessed using a sleep recording — known as polysomnography — on two occasions, approximately five years apart, in 1995-1998 and again in 2001-2003.
Many people showed a reduction in their deep slow-wave sleep over the years, as is to be expected with aging. Conversely, the amount of deep sleep in some people remained stable or even increased.
Our team of researchers from the Framingham Heart Study followed 346 participants aged 60 and over for a further 17 years to observe who developed dementia and who did not.
Progressive loss of deep sleep over time was associated with an increased risk of dementia, whatever the cause, and particularly Alzheimer’s type dementia. These results were independent of many other risk factors for dementia.
Although our results do not prove that loss of deep sleep causes dementia, they do suggest that it could be a risk factor in the elderly. Other aspects of sleep may also be important, such as its duration and quality.
Strategies to improve deep sleep
Knowing the impact of a lack of deep sleep on cognitive health, what strategies can be used to improve it?
First and foremost, if you’re experiencing sleep problems, it’s worth talking to your doctor. Many sleep disorders are underdiagnosed and treatable, particularly through behavioural (i.e. non-medicinal) approaches.
Adopting good sleep habits can help, such as going to bed and getting up at consistent times or avoiding bright or blue light in bed, like that of screens.
You can also avoid caffeine, limit your alcohol intake, maintain a healthy weight, be physically active during the day, and sleep in a comfortable, dark and quiet environment.
The role of deep sleep in preventing dementia remains to be explored and studied. Encouraging sleep with good lifestyle habits could have the potential to help us age in a healthier way.
![]()
Andrée-Ann Baril received funding from the Sleep Research Society Foundation, the Alzheimer Society of Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Banting Postdoctoral Fellowships, the Fondation de l’Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur de Montréal, the Université de Montréal and speaking fees from Eisai.
Matthew Pase received funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, National Institute on Aging, Dementia Australia, Alzheimer’s Association, National Heart Foundation of Australia, Australian Research Council, Stroke Foundation, Brain Foundation, Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, Rebecca L Cooper Medical Research Foundation, and Bethlehem Griffiths Research Foundation.
























