Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States.
Since researchers first established the link between diet, cholesterol and heart disease in the 1950s, risk for heart disease has been partly assessed based on a patient’s cholesterol levels, which can be routinely measured via blood work at the doctor’s office.
However, accumulating evidence over the past two decades demonstrates that a biomarker called C-reactive protein – which signals the presence of low-grade inflammation – is a better predictor of risk for heart disease than cholesterol.
As a result, in September 2025, the American College of Cardiology published new recommendations for universal screening of C-reactive protein levels in all patients, alongside measuring cholesterol levels.
Table of Contents
What is C-reactive protein?
C-reactive protein is created by the liver in response to infections, tissue damage, chronic inflammatory states from conditions like autoimmune diseases, and metabolic disturbances like obesity and diabetes. Essentially, it is a marker of inflammation – meaning immune system activation – in the body.
C-reactive protein can be easily measured with blood work at the doctor’s office. A low C-reactive protein level – under 1 milligram per deciliter – signifies minimal inflammation in the body, which is protective against heart disease. An elevated C-reactive protein level of greater than 3 milligrams per deciliter, signifies increased levels of inflammation and thus increased risk for heart disease. About 52% of Americans have an elevated level of C-reactive protein in their blood.
Research shows that C-reactive protein is a better predictive marker for heart attacks and strokes than “bad,” or LDL cholesterol, short for low-density lipoprotein, as well as another commonly measured genetically inherited biomarker called lipoprotein(a). One study found that C-reactive protein can predict heart disease just as well as blood pressure can.
Why does inflammation matter in heart disease?
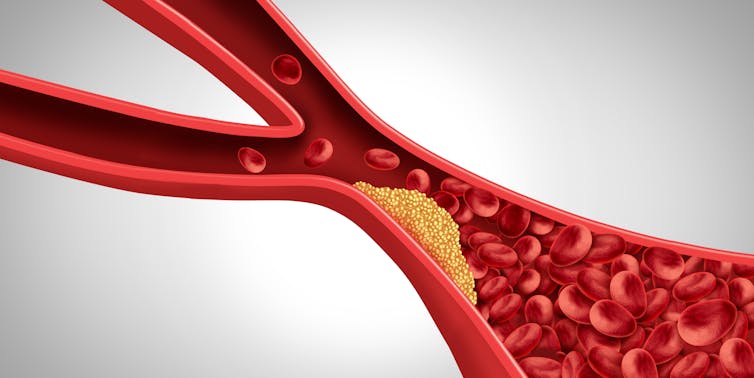
Inflammation plays a crucial role at every stage in the development and buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries, which causes a condition called atherosclerosis that can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
From the moment a blood vessel is damaged, be it from high blood sugar or cigarette smoke, immune cells immediately infiltrate the area. Those immune cells subsequently engulf cholesterol particles that are typically floating around in the blood stream to form a fatty plaque that resides in the wall of the vessel.
This process continues for decades until eventually, one day, immune mediators rupture the cap that encloses the plaque. This triggers the formation of a blood clot that obstructs blood flow, starves the surrounding tissues of oxygen and ultimately causes a heart attack or stroke.
Hence, cholesterol is only part of the story; it is, in fact, the immune system that facilitates each step in the processes that drive heart disease.
wildpixel/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Can diet influence C-reactive protein levels?
Lifestyle can significantly influence the amount of C-reactive protein produced by the liver.
Numerous foods and nutrients have been shown to lower C-reactive protein levels, including dietary fiber from foods like beans, vegetables, nuts and seeds, as well as berries, olive oil, green tea, chia seeds and flaxseeds.
Weight loss and exercise can also reduce C-reactive protein levels.

monticelllo/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Does cholesterol still matter for heart disease risk?
Though cholesterol may not be the most important predictor of risk for heart disease, it does remain highly relevant.
However, it’s not just the amount of cholesterol – or more specifically the amount of bad, or LDL, cholesterol – that matters. Two people with the same cholesterol level don’t necessarily have the same risk for heart disease. This is because risk is determined more so by the number of particles that the bad cholesterol is packaged into, as opposed to the total mass of bad cholesterol that’s floating around. More particles means higher risk.
That is why a blood test known as apolipoprotein B, which measures the number of cholesterol particles, is a better predictor of risk for heart disease than measurements of total amounts of bad cholesterol.
Like cholesterol and C-reactive protein, apolipoprotein B is also influenced by lifestyle factors like exercise, weight loss and diet. Nutrients like fiber, nuts and omega-3 fatty acids are associated with a decreased number of cholesterol particles, while increased sugar intake is associated with a larger number of cholesterol particles.
Furthermore, lipoprotein(a), a protein that lives in the wall surrounding cholesterol particles, is another marker that can predict heart disease more accurately than cholesterol levels. This is because the presence of lipoprotein(a) makes cholesterol particles sticky, so to speak, and thus more likely to get trapped in an atherosclerotic plaque.
However, unlike other risk factors, lipoprotein(a) levels are purely genetic, thus not influenced by lifestyle, and need only be measured once in a lifetime.
What’s the best way to prevent heart disease?
Ultimately, heart disease is the product of many risk factors and their interactions over a lifetime.
Therefore, preventing heart disease is way more complicated than simply eating a cholesterol-free diet, as once thought.
Knowing your LDL cholesterol level alongside your C-reactive protein, apolipoprotein B and lipoprotein (a) levels paints a comprehensive picture of risk that can hopefully help motivate long-term commitment to the fundamentals of heart disease prevention. These include eating well, exercising consistently, getting adequate sleep, managing stress productively, maintaining healthy weight and, if applicable, quitting smoking.

























