
Now that kids ages 5 to 11 are eligible for COVID-19 vaccination and the number of fully vaccinated people in the U.S. is rising, many people may be wondering what the endgame is for COVID-19.
Early on in the pandemic, it wasn’t unreasonable to expect that SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) might just go away, since historically some pandemic viruses have simply disappeared.
For instance, SARS-CoV, the coronavirus responsible for the first SARS pandemic in 2003, spread to 29 countries and regions, infecting more than 8,000 people from November 2002 to July 2003. But thanks to quick and effective public health interventions, SARS-CoV hasn’t been observed in humans in almost 20 years and is now considered extinct.
On the other hand, pandemic viruses may also gradually settle into a relatively stable rate of occurrence, maintaining a constant pool of infected hosts capable of spreading the virus to others. These viruses are said to be “endemic.”
Examples of endemic viruses in the United States include those that cause the common cold and the seasonal flu that appear year after year. Much like these, the virus that causes COVID-19 likely won’t die out, and most experts now expect it to become endemic.
We are a team of virologists and immunologists from the University of Colorado Boulder studying animal viruses that infect humans. An essential focus of our research is to identify and describe the key adaptations that animal viruses require to persist in the human population.
Table of Contents
What determines which viruses become endemic?
So why did the first SARS virus from 2003 (SARS-CoV) go extinct while this one (SARS-CoV-2) may become endemic?
The ultimate fate of a virus depends on how well it maintains its transmission. Generally speaking, viruses that are highly contagious, meaning that they spread really well from one person to the next, may never die out on their own because they are so good at finding new people to infect.
When a virus first enters a population with no immunity, its contagiousness is defined by scientists using a simple mathematical term, called R0, which is pronounced “R-naught.” This is also referred to as the reproduction number. The reproduction number of a virus represents how many people, on average, are infected by each infected person. For example, the first SARS-CoV had an R0 of about 2, meaning that each infected person passes the virus to two people on average. For the delta variant strain of SARS-CoV-2, the R0 is between 6 and 7.
The goal for public health authorities is to slow the rate by which viruses spread. Universal masking, social distancing, contact tracing and quarantines are all effective tools to reduce the spread of respiratory viruses. Since SARS-CoV was poorly transmissible, it just took a little bit of public health intervention to drive the virus to extinction. Given the highly transmissible nature of the delta variant, the challenge for eliminating the virus will be much greater, meaning that the virus is more likely to become endemic.

Bryan R. Smith/AFP via Getty Images
Is COVID-19 ever going away?
It’s clear that SARS-CoV-2 is very successful at finding new people to infect, and that people can get infected after vaccination. For these reasons, the transmission of this virus is not expected to end. It’s important that we consider why SARS-CoV-2 moves so easily from one person to the next, and how human behavior plays into that virus transmission.
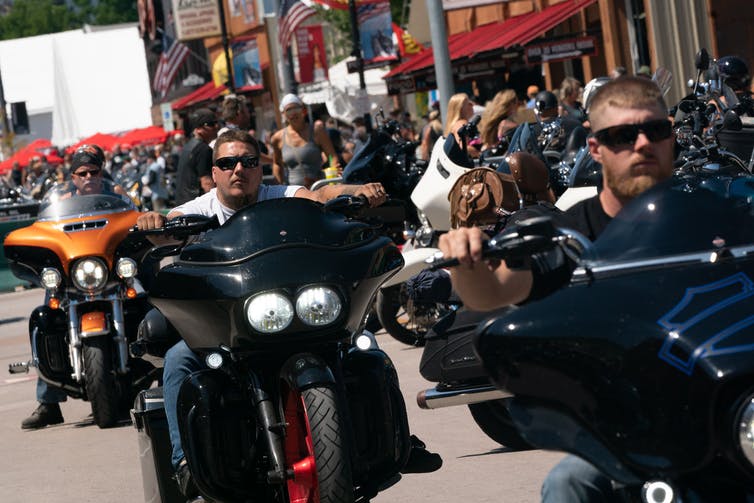
SARS-CoV-2 is a respiratory virus that is spread through the air and is efficiently transmitted when people congregate. Critical public health interventions, like mask use and social distancing, have been key in slowing the spread of disease. However, any lapse in these public health measures can have dire consequences. For instance, a 2020 motorcycle rally brought together nearly 500,000 people in Sturgis, South Dakota, during the early phases of the pandemic. Most of the attendees were unmasked and not practicing social distancing. That event was directly responsible for an increase in COVID-19 cases in the state of South Dakota and nationwide. This shows how easily the virus can spread when people let their guard down.
The virus that causes COVID-19 is often associated with superspreading events, in which many people are infected all at once, typically by a single infected individual. In fact, our own work has shown that just 2% of the people infected with COVID-19 carry 90% of the virus that is circulating in a community. These important “supercarriers” have a disproportionately large impact on infecting others, and if they aren’t tracked down before they spread the virus to the next person, they will continue to sustain the epidemic. We currently don’t have a nationwide screening program geared toward identifying these individuals.
Finally, asymptomatically infected people account for roughly half of all infections of COVID-19. This, when coupled with a broad range of time in which people can be infectious – two days before and 10 days after symptoms appear – affords many opportunities for virus transmission, since people who don’t know they are sick generally take few measures to isolate from others.
The contagious nature of SARS-CoV-2 and our highly interconnected society constitute a perfect storm that will likely contribute to sustained virus spread.
Justin Sullivan/Getty Images News via Getty Images
What will our future with COVID-19 look like?
Given the considerations discussed above and what we know about COVID-19 so far, many scientists believe that the virus that causes COVID-19 will likely settle into endemic patterns of transmission. But our inability to eradicate the virus does not mean that all hope is lost.
Our post-pandemic future will heavily depend on how the virus evolves over the coming years. SARS-CoV-2 is a completely new human virus that is still adapting to its new host. Over time, we may see the virus become less pathogenic, similar to the four coronaviruses that cause the common cold, which represent little more than a seasonal nuisance.
Global vaccination programs will have the greatest impact on curbing new cases of the disease. However, the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine campaign so far has touched only a small percentage of people on the planet. In addition, breakthrough infections in vaccinated people still occur because no vaccine is 100% effective. This means that booster shots will likely be needed to maximize vaccine-induced protection against infection.
With global virus surveillance and the speed at which safe and effective vaccines have been developed, we are well poised to tackle the ever-evolving target that is SARS-CoV-2. Influenza is endemic and evolves quickly, but seasonal vaccination enables life to go on as normal. We can expect the same for SARS-CoV-2 – eventually.
How will we know if and when SARS-CoV-2 becomes endemic?
Four seasonal coronaviruses circulate in humans endemically already. They tend to recur annually, usually during the winter months, and affect children more than adults. The virus that causes COVID-19 has not yet settled down into these predictable patterns and instead is flaring up unpredictably around the globe in ways that are sometimes difficult to predict.
[Over 115,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today.]
Once rates of SARS-CoV-2 stabilize, we can call it endemic. But this transition may look different based on where you are in the world. For instance, countries with high vaccine coverage and plentiful boosters may soon settle into predictable spikes of COVID-19 during the winter months when the environmental conditions are more favorable to virus transmission. In contrast, unpredictable epidemics may persist in regions with lower vaccination rates.
![]()
Sara Sawyer is a co-founder of Darwin Biosciences, an infectious disease diagnostics company based in Boulder, CO. She receives funding from the National Institutes of Health.
Cody Warren receives funding from the National Institutes of Health.
Arturo Barbachano-Guerrero does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.























