A feral kitten in Omaha, Nebraska, tested positive for rabies in November 2023. It died of the raccoon variant of the virus, which is typically found only in the Appalachian Mountains. Detecting this variant hundreds of miles away in the Midwest raised concerns about a potential outbreak and launched a public health task force to vaccinate all raccoons in the area.
While the case was likely contained, a better understanding of how rabies is transmitted can help prevent future outbreaks. Researchers Rodney Rohde and Charles Rupprecht explain how rabies vaccination works and how to protect yourself from infection.
Table of Contents
What causes rabies?
Rabies is an ancient viral disease that has been around for thousands of years. Considered a neglected tropical disease, rabies typically occurs in poorer communities without the infrastructure for adequate surveillance, prevention and control.
Rabies is unpredictable. Stages of infection include an incubation period that ranges from days to months, early flu-like symptoms, a period of severe neurological effects, coma and then death. Common early-stage symptoms in people, such as fatigue, fever and nausea, are often nonspecific. Neurological symptoms can involve aggression, confusion, difficulty swallowing and paralysis.
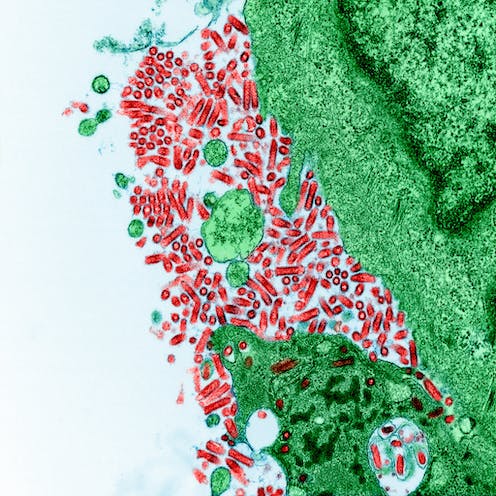
The pathogens that cause rabies belong to a genus of viruses called Lyssavirus that target warm-blooded vertebrates. Although researchers believe that all mammals are susceptible to infection, only certain animals are reservoirs: environments, habitats or populations where a pathogen can live, multiply and transmit. In the U.S., the highest-risk animal reservoirs for rabies are skunks, bats, foxes, coyotes and raccoons.
Most people who become infected with rabies get it from an animal bite. Less common routes include contact with open wounds or the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose or mouth. Once the virus enters the body, it can begin replicating in muscle tissue or after traveling directly to the brain. Once it spreads to other organs, patients typically die of brain inflammation.
Are rabies cases increasing?
Measuring the global burden of rabies is difficult because surveillance is often inadequate.
While human incidence of rabies are rare in the U.S., averaging one to three cases per year, this disease causes tens of thousands of deaths worldwide annually.
Rabies rates in animals vary each year. During 2021, 54 U.S. jurisdictions reported 3,663 rabid animals, an 18.2% decrease from the previous year. Lower- and middle-income countries, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic, have experienced disruptions to animal vaccination for rabies due to vaccine production and access issues and increased feral animal populations.
Human rabies cases have risen in several countries because of multiple ecological and socioeconomic factors. For example, in China, rabies cases are associated with proximity to urban populations and transportation hubs. The closer a susceptible animal is to a community experiencing an outbreak, the greater the likelihood for spread.
Increased temperatures due to climate change are also linked to increased rabies transmission because of changes in animal ranges. For example, as regions warm, the relative distribution and abundance of certain reservoirs, such as tropical species like vampire bats, may increase. Rising Arctic temperatures may increase how often red and Arctic foxes interact and lead to outbreaks.
Higher rates of interactions between humans and animals, as well as lower levels of rabies education and prevention measures, are also linked to an increased risk of infection.
Has controlling rabies in wildlife been successful?
Prior attempts to control rabies include animal culling and vaccination. Culling animal populations did not lead to reduced infection. Rather, it raised significant economic, ecological and ethical concerns. Besides killing likely healthy animals, culling also isn’t cost-effective.
Animal vaccination, on the other hand, can protect both animals and humans with minimal risk and reduced costs. Oral rabies vaccination of wildlife began during the 1970s with the distribution of vaccine-laden baits in the local environment. Officials saw success in rabies control among coyote, fox and raccoon populations in Europe and North America.

CDC/Nicholas S. Tenorio, Health Communication Specialist
We both participated in the inaugural oral rabies vaccination campaign in Texas. This effort eventually led to the elimination of canine rabies in the state.
Oral vaccines are also being considered for the prevention and control of rabies in animals in other countries, such as dogs in India and Thailand.
How do rabies vaccines work?
There is no proven treatment for rabies, so prevention through education and vaccination is critical. Rabies can be prevented by avoiding exposure or receiving vaccination before or after an exposure.
Preexposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, involves exposing the immune system to a harmless version of the virus to prevent a future infection. For people who work in high-risk occupations, such as wildlife biologists, veterinarians and animal control personnel, two doses of a rabies vaccine can offer significant protection.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends a booster dose for people at elevated risk of exposure. People traveling to areas with a high prevalence of rabies may also want to consider vaccination.
Postexposure prophylaxis, or PEP, means taking a vaccine or medications to prevent an infection as soon as possible after exposure. In most cases, this involves a dose of human rabies immune globulin, or HRIG, as well as a rabies vaccine dose on the day of exposure.
Also known as passive immunization, HRIG gives your body the antibodies to neutralize rabies virus until your immune system can produce its own antibodies. Three more doses of the rabies vaccine are given three to 14 days after exposure. People who are immunocompromised may receive a fifth dose as well.
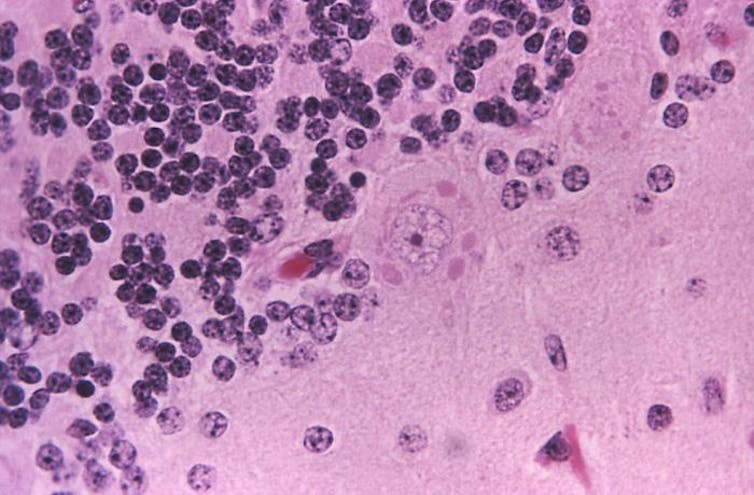
CDC/Dr. Daniel P. Perl
Regular and appropriate pet and livestock vaccinations are also important to help curb rabies virus exposures. Animals typically receive a yearly rabies booster.
There are several new rabies vaccines for animals and people in development to improve their safety, cost and efficacy. Researchers are also developing treatments to control rabies when the infection reaches the central nervous system.
How do you protect yourself from rabies?
Some people may not realize they were bitten by an animal if the bites are small. Because of the long incubation period of the virus, they also may not recall a previous interaction with an infected animal.
Laboratory tests can confirm whether an animal has rabies, as well as which rabies virus variant is present. A physician may begin vaccination even without laboratory confirmation based on the risk factors of a case. For example, since most recent fatal rabies cases in the U.S. have been from unknown bat bites, rabies vaccination is recommended after any suspected bat exposure.
There are many practical ways to protect yourself from rabies such as:
- Vaccinating and supervising your pets.
- Never handling wild animals that seem to be acting strangely.
- Not touching sick, injured or dead animals.
- Never attempting to feed wildlife.
- Treating animals respectfully. Do not tease an animal, disturb its sleep or handle its offspring.
- Always reporting a bite to an animal control officer, game warden or health care professional.
World Rabies Day, which marks the death of rabies vaccine developer Louis Pastuer, is Sept. 28.
![]()
Rodney E. Rohde has received funding from the American Society of Clinical Pathologists, American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science, U.S. Department of Labor (OSHA), and other public and private entities/foundations. Rohde is affiliated with ASCP, ASCLS, ASM, and serves on several scientific advisory boards.
Charles Rupprecht is a global biomedical consultant for academia, government, industry and NGOs. He is affiliated with LYSSA LLC.
























