
Climate change can exacerbate a full 58% of the infectious diseases that humans come in contact with worldwide, from common waterborne viruses to deadly diseases like plague, our new research shows.
Our team of environment and health scientists reviewed decades of scientific papers on all known pathogenic disease pathogens to create a map of the human risks aggravated by climate-related hazards.
The numbers were jarring. Of 375 human diseases, we found that 218 of them, well over half, can be affected by climate change.
Flooding, for example, can spread hepatitis. Rising temperatures can expand the life of mosquitoes carrying malaria. Droughts can bring rodents infected with hantavirus into communities as they search for food.
With climate change influencing more than 1,000 transmission pathways like those and climate hazards increasingly globally, we concluded that expecting societies to successfully adapt to all of them isn’t a realistic option. The world will need to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions that are driving climate change to reduce these risks.
Table of Contents
Mapping climate health hazards
To be able to prevent global health crises, humanity needs a comprehensive understanding of the pathways and the magnitude with which climate change might affect pathogenic diseases.
We focused on 10 climate-related hazards linked to rising greenhouse gas emissions: atmospheric warming, heat waves, drought, wildfires, heavy precipitation, flooding, storms, sea-level rise, ocean warming and land cover change. Then we looked for studies discussing specific and quantifiable observations of human disease occurrences linked to those hazards.
In total, we reviewed over 77,000 scientific papers. Of those, 830 papers had a climatic hazard affecting a specific disease in an explicit place and/or time, allowing us to create a database of climatic hazards, transmission pathways, pathogens and diseases. An interactive map of every pathway between hazard and pathogen is available online.
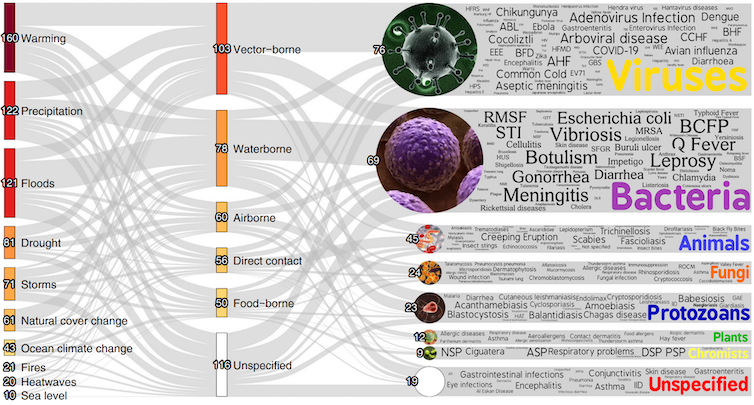
Camilo Mora, CC BY-ND
The largest number of diseases aggravated by climate change involved vector-borne transmission, such as those spread by mosquitoes, bats or rodents. Looking at the type of climate hazard, the majority were associated with atmospheric warming (160 diseases), heavy precipitation (122) and flooding (121).
How climate influences pathogen risk
We found four key ways climatic hazards interact with pathogens and humans:
1) Climate-related hazards bring pathogens closer to people.
In some cases, climate-related hazards are shifting the ranges of animals and organisms that can act as vectors for dangerous pathogenic diseases.
For example, warming or changes in precipitation patterns can alter the distribution of mosquitoes, which are vectors of numerous human pathogenic diseases. In recent decades, geographic changes in outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue have been linked to these climatic hazards.
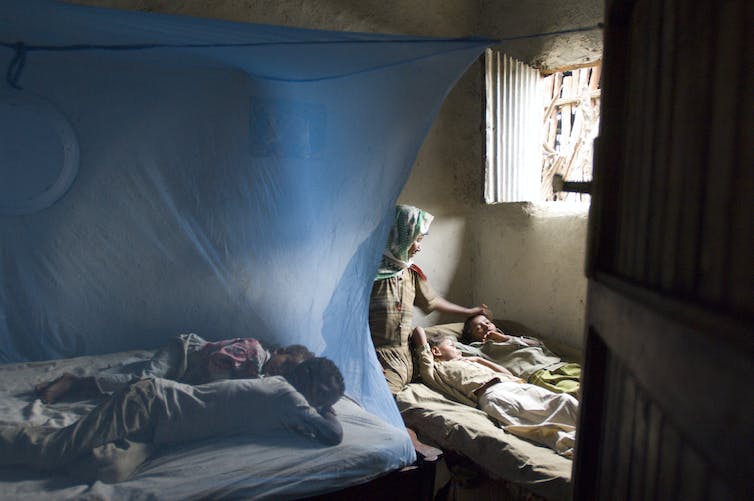

Louise Gubb/Corbis via Getty Images
2) Climate-related hazards bring people closer to pathogens.
Climate disasters can also alter human behavior patterns in ways that increase their chances of being exposed to pathogens. For example, during heat waves, people often spend more time in water, which can lead to an increase in waterborne disease outbreaks.
Notably, Vibrio-associated infections increased substantially in Sweden and Finland following a heat wave in northern Scandinavia in 2014.
3) Climate-related hazards enhance pathogens.
In some cases, climate-related hazards have led to either environmental conditions that can increase opportunities for pathogens to interact with vectors or increase the ability of pathogens to cause severe illness in humans.
For example, standing water left by heavy precipitation and flooding can provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes, leading to increased transmission of diseases such as yellow fever, dengue, malaria, West Nile fever and leishmaniasis.
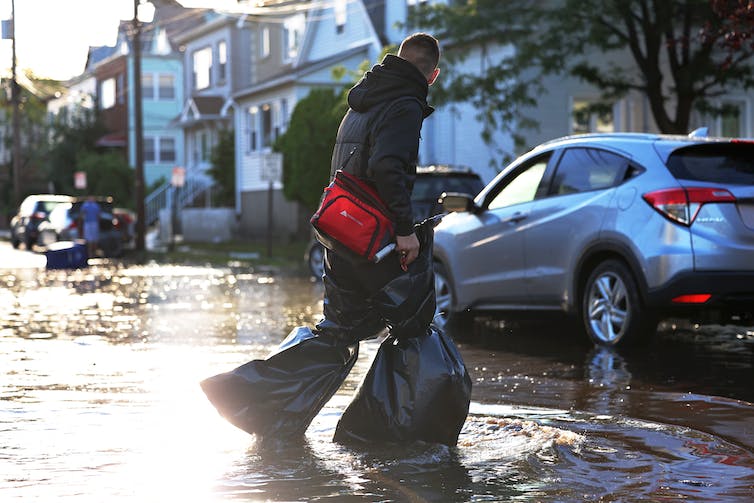

Michael M. Santiago/Getty Images
Studies have shown that rising temperatures may also help viruses become more resistant to heat, resulting in increased disease severity as pathogens become better able to adapt to fever in the human body.
For instance, studies have suggested that rising global temperatures are leading to increased heat tolerance of fungal pathogens. The sudden appearance on multiple continents of treatment-resistant human infections of Candida auris, a fungus that was previously nonpathogenic to humans, has been associated with increasing global temperatures. Similarly, fungi in urban environments have been shown to be more heat tolerant than those in rural areas, which tend to be cooler.

Arturo Casadevall, Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis, Vincent Robert via Wikimedia, CC BY-ND
4) Climate-related hazards weaken the body’s ability to cope with pathogens.
Climate-related hazards can affect the human body’s ability to cope with pathogens in two key ways. They can force people into hazardous conditions, such as when disaster damage leads to people living in crowded conditions that might lack good sanitation or increase their exposure to pathogens.
Hazards can also reduce the body’s capacity to fight off pathogens, through malnutrition, for example. Living through climatic hazards may also induce increased cortisol production from stress, leading to a reduction in the human body’s immune response.
What to do about it
Climate change presents a significant threat to human lives, health and socioeconomic well-being. Our map shows just how extensive that threat can be. In our view, to dial back the risk, humanity will have to put the brakes on the human-caused greenhouse gas emissions fueling global warming.
![]()
The authors do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.





























