
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Not only does it act as the first line of defence against external stressors such as environmental toxins, pathogens and pollutants, our skin can also reveal much about our internal health.
Research has shown that the gut and skin are constantly communicating through the “gut-skin axis.” This means that itchy, red, bumpy or scaly skin may be associated with something happening in the gut.
Table of Contents
Intestinal bacteria and skin conditions
There is increasing clinical evidence linking changes in the composition of the gut microbiome to the development of various skin diseases.
The human gut microbiome consists of a population of microorganisms, collectively referred to as microbiota, that live in the gastrointestinal tract. The gut microbiome has many different functions, such as protecting us against infections, training the immune system, synthesizing vitamins and digesting natural products such as carbohydrates.
Many factors influence the composition, richness and function of the gut microbiota, including stress, diet, alcohol consumption, exercise and antibiotic use.
However, when the intricate balance between beneficial and unfavourable microbiota in the gut is changed — also referred to as “dysbiosis” — it can cause the gut barrier to become leaky. This is called leaking gut syndrome, a condition where the gut becomes increasingly permeable and allows microbial toxins, food antigens (minuscule food particles) and harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream.
This can cause changes in how the immune system reacts, which can result in the development of inflammatory skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, rosacea and acne.
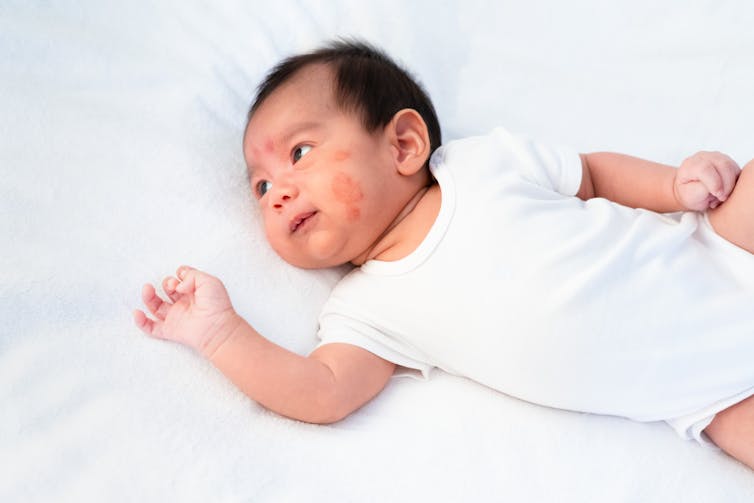
Atopic dermatitis (eczema)

(Shutterstock)
Atopic dermatitis, also referred to as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory condition that most frequently occurs in children up to the age of five. Studies have demonstrated that the gut microbiome of individuals with eczema contains a lower number of Bacteroidetes and Bifidobacteria, which are bacteria that work to protect the intestines against the colonization of pathogens.
In addition, the number of bacteria in the gut that produce butyrate — a short-chain fatty acid that helps to support the integrity and function of our gut epithelial barrier — has been found to be lower in infants with eczema. These short-chain fatty acids also have anti-inflammatory effects and act as immunomodulators that help to regulate our immune responses.
4 factors that can influence gut microbiota balance
Emerging research on the microbiome has made it clear that the microorganisms in our gut play a key role in our immune responses, metabolism and physiology. Researchers have investigated several factors that can influence the balance of microbiota in our gut, and ways to re-establish gut health if dysbiosis occurs.
1 — Early-life colonization of the gut microbiome
Infancy and early childhood are crucial stages for the development of both the gut microbiome and the immune system. With approximately 80 per cent of human immune cells located in the lymphoid tissue around the gastrointestinal tract, the gut can be considered the centre of the immune system.
The colonization of the gut microbiome by microorganisms begins at birth. Babies delivered vaginally are first introduced to the microorganisms found in their mother’s genitourinary tract. For example, the maternal microbiome provides the infant intestinal tract with its first source of Escherichia coli, Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides. In addition, exposure to breast milk often provides infants with another source of microorganisms, such as Streptococci and Lactobacillus.
2 — Antibiotics
(Shutterstock)
Antibiotics are medications that help our body to fight against infections by killing bacteria and slowing their growth. Antibiotics are often necessary and can be life-saving. However, antibiotic treatments do not just target the bacteria that cause infection. They also harm the beneficial bacteria found in our gut.
Overall, it can take more than two years for the microbiome to recover after being exposed to antibiotics. In some cases, bacterial diversity in the gut microbiome may never completely return back to normal. This finding has been reported with both oral and intravenous antibiotic treatments. It is therefore important to take antibiotics appropriately and only when necessary. This is especially important in the area of dermatology, where skin conditions such as eczema may initially be mistaken for an infection and treated unnecessarily with antibiotics.
3 — Probiotics and prebiotics
The gut microbiome can further be strengthened by taking probiotics and prebiotics, helping in the management of skin conditions such as eczema.
Probiotics are live beneficial organisms. They work by competitively binding to the cells of the intestinal epithelium, which makes up the lining of the small and large intestine. In doing so, probiotics help to prevent pathogens from invading the body. This competitive binding goes hand-in-hand with the production of bacteriocins, an antibiotic-like protein produced by probiotic organisms. These bacteriocins further suppress pathogen development.
Prebiotics are food substances that cannot be digested or absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Similar to probiotics, prebiotics help to strengthen the intestinal barrier by supporting the production of short-chain fatty acids and enhancing the body’s immune responses.
While probiotics and prebiotics can be used to achieve a beneficial balance of microbiota in the gut before illness, it is much more difficult to restore this balance during or after illness. The use of probiotics and prebiotics can therefore be used as a complementary intervention to the treatment of people with conditions such as eczema.
4 — Diet
Finally, let’s look at the impact of diet on the gut microbiome.
Research has found that gluten can be a source of different health problems, including dysbiosis of the gut. Negative health effects are especially apparent in people who are hypersensitive to gluten or those who live with celiac disease.
Gluten sensitivity and leaky gut are part of a positive feedback loop, both reinforcing one another. This means that when people who are hypersensitive to gluten or celiac patients eat gluten, it can harm their intestinal barrier and cause the gut to become increasingly permeable, or “leaky.” In turn, foreign particles are able to escape from the gut into the bloodstream, causing the immune system to be on high-alert and send out waves of inflammation throughout the body.
These inflammatory reactions can give rise to skin conditions such as eczema. However, at the same time, a leaky gut may cause increased sensitivity to gluten, thereby reinforcing the initial trigger of leaky gut syndrome and causing further harm to the intestinal barrier.

(Shutterstock)
Research has also revealed that foods high in added sugars, gluten, alcohol, or nightshade vegetables such as potatoes and peppers, can change the composition of the gut microbiota. For example, eating too much sugar can lead to the overgrowth of E. coli in the intestines, negatively affecting the function of the microbiome. Overall, these foods can cause your intestinal lining to become irritated and give rise to dysbiosis in the gut, which decreases microbial diversity and increases inflammation.
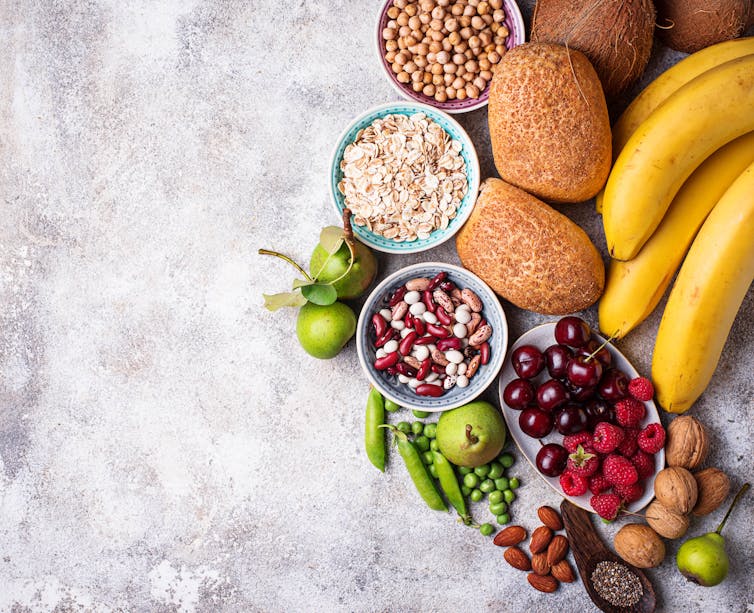
Instead, eating fibre-rich foods can help restore the balance of the gut microbiota, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut and lower the number of signalling molecules (cytokines) that promote inflammation. These foods can include fruits (such as raspberries, pears, bananas), complex carbohydrates (such as brown rice, whole-grain bread and legumes) and vegetables (such as broccoli, green peas and brussels sprouts). Fermented foods such as kombucha also help to increase the diversity of bacteria in your gut.
Based on the growing link between the development of inflammatory skin diseases and gut microbiome dysbiosis, it is important to look after your gut health. While early-life colonization of the gut microbiome and the intake of antibiotics are not always in our control, we can nevertheless support our gut by being mindful of diet and using probiotics and prebiotics.
![]()
The authors do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
























