
When people get into their 40s and beyond, their close-up vision starts to worsen. For many people, cranking up the font size on a phone or maxing out the brightness on a computer is the only way to be able to read some text.
This condition is known as presbyopia, and it affects around 128 million people in the U.S. and more than a billion people worldwide.
In late 2021, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a new eye drop medication to treat presbyopia. As an optometrist, I was initially skeptical. Prior to the release of these eye drops – called Vuity – people would either need glasses, contacts or eye surgery to alleviate presbyopia. But after learning how these eye drops work, I recognized that for many people, they could offer an easier and safer way to see clearly again.
ttsz/iStock via Getty Images
Table of Contents
How eyes focus
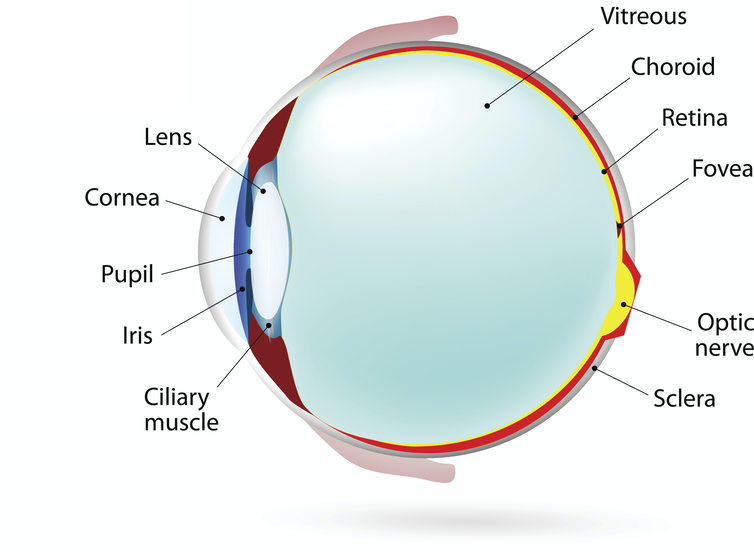
Many parts of the human eye interact with incoming light to produce a clear image.
The first thing light hits is the cornea, the clear outer layer that initially bends the light. Then light passes through the iris and pupil, which can shrink or grow to let more or less light into the inside of the eye. It then travels through the lens, which further bends the light and precisely focuses it onto the center of the retina. Finally, the light signal is transferred to the optic nerve at the back of the eye, for the brain to interpret as an image.
To produce a clear image, your eyes need to adjust to how far away an object is. Your eyes take three major steps to focus on objects close to your face: your eyes point toward the object you want to look at, your lenses change shape and your pupils constrict.
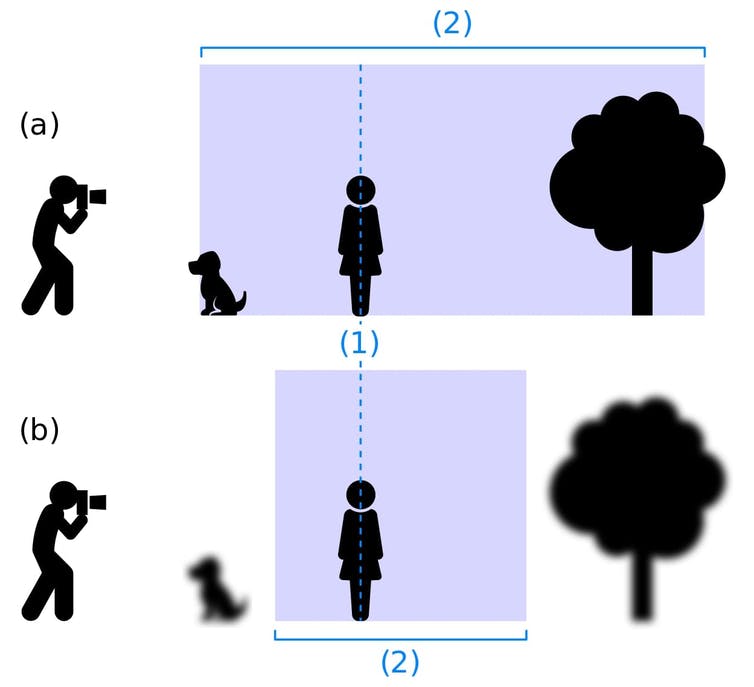
Once you point your gaze at what you’re interested in, a small muscle in the eye contracts, which changes the shape of the lens to make it thicker. The thicker the lens is, the more the light bends as it passes through. At the same time, your pupils constrict to block some of the incoming light from other objects in the distance. When light bounces off an object and enters your eye, the rays of light at the center are what provide a clear image. Blocking the scattering light by constricting the pupil helps to sharpen the image of close objects.
You can simulate this process using a camera on your cellphone. First, point the camera at something in the distance. Then, move your thumb into the image, holding it about 6 inches away. Your thumb will start off blurry, but as the camera’s lens changes shape, your thumb will come into focus.

BruceBlaus via WikimediaCommons, CC BY-SA
What is presbyopia?
Presbyopia is the inability of the eyes to focus on close objects, which results in blurry images. It begins when people are in their 40s and progresses until it plateaus around the age of 60.
Researchers know that age is the main driver of presbyopia, but there is an ongoing debate over the mechanical causes at its root.
One theory suggests that as lenses age, they get heavier and can’t change shape as easily. Another theory suggests that the muscle that pull on the lens become weaker with age. I suspect presbyopia likely occurs due to a combination of both. Regardless of the cause, the result is that when looking at close objects, people’s eyes are no longer able to bend incoming light enough to direct it at the center of the retina. Instead, the light is focused at a place behind the retina, resulting in blurry vision.
How the eye drops work
Remember, there are two major things an eye does to focus on close objects: the lens changes shape and the pupil gets smaller. Since presbyopia limits the ability of the lens to change shape, these eye drops compensate by causing the pupil to get smaller. Constricting the pupil reduces the amount of light scatter. This makes it so that the light entering the eye is better concentrated onto the retina, thus creating a wider range of distances where objects are in focus and allowing people to see both close and far objects clearly.
MikeRun via WikimediaCommons, CC BY-SA
Once you put the drops in your eyes, it takes about 15 minutes for the active ingredient, pilocarpine, to begin working. Pilocarpine is a medication that was first discovered in the late 1800s, and can treat conditions such as glaucoma and ocular hypertension. The effect on pupils lasts for about six hours.
Smaller pupils mean that less light gets into the eye. While this isn’t a problem during the day when there is a lot of sun, it can cause difficulty seeing in low-lighting conditions. Aside from these downsides, the most common side effects of the drops are headache and red eyes.
Presbyopia in the future
Vuity is currently approved for once-daily use in each eye. A bottle will cost around $80, requires a prescription and will last for nearly a month if used daily. For some people, it could be a great alternative or adjunct to glasses or surgery.
While Vuity may be the first FDA-approved eye drops to treat presbyopia, researchers are studying a number of other approaches. Some are developing eye drops that include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to help constrict the pupil – similarly to Vuity. Other teams are studying drops that soften and reduce the weight of the lens to promote easier focusing. Finally, some early research has shown that pulsed electrostimulation of eye muscles can help strengthen them and improve people’s ability to bend their lenses.
The future of presbyopia treatment is exciting as researchers work on many potential ways to overcome this universal condition of old age. For now, Vuity – while not a magic cure for everyone with presbyopia – is an innovative option and may be worth asking your eye doctor about.
[Understand new developments in science, health and technology, each week. Subscribe to The Conversation’s science newsletter.]
![]()
Robert Bittner does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.






















